
Menu

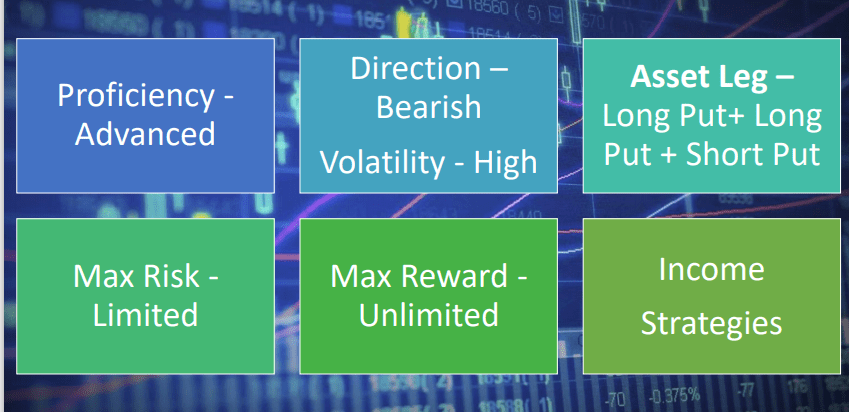
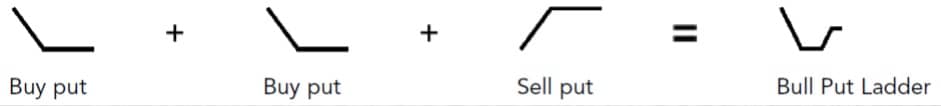
Outlook
Rationale
Effect of Time Decay
Time Period to Trade
Breakeven Down = [Lower strike – Maximum risk]
Breakeven Up = [Higher strike + net debit] (or – net credit)
Steps In
Steps Out
Exiting the Position
Mitigating a Loss
Advantages
Disadvantages
Share this Content
© 2021 All rights reserved
Ask Your Query