
Menu

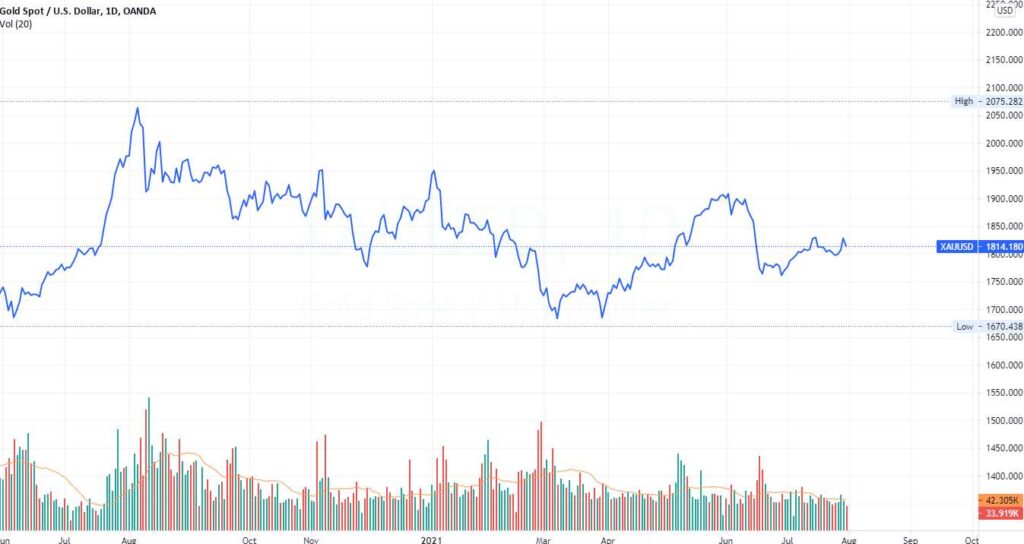
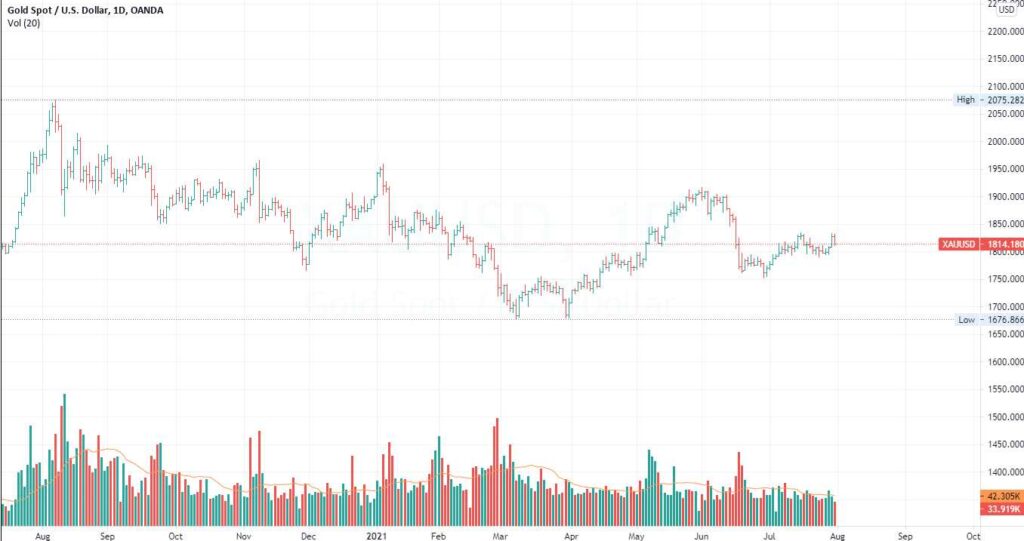
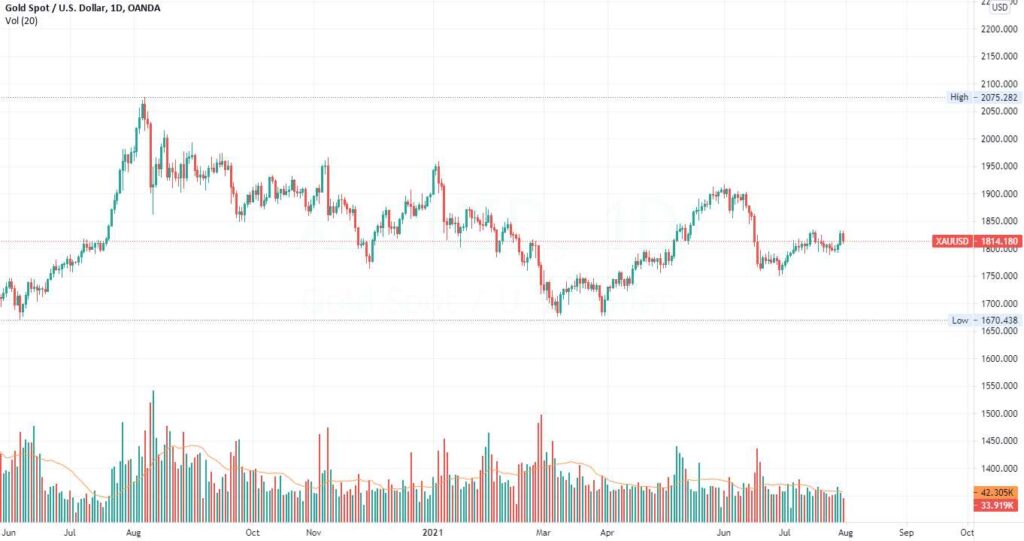
A chart is a graphical representation of price and volume movements of a stock over a certain period of time.
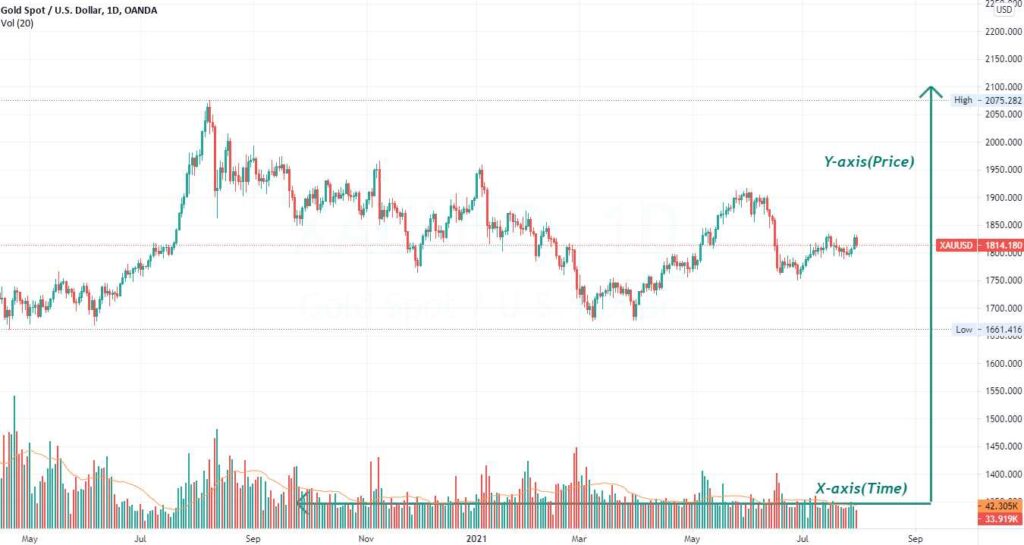
Some well known form of charts in technical analysis are –
Share this Content
© 2021 All rights reserved
Ask Your Query