
Menu

A house loan, also known as a housing loan, is a sum obtained from a bank or a non-bank financial institution (NBFC) for the purpose of purchasing, constructing, repairing, or renovating a residential property over a set period of time. Lenders impose interest on the amount borrowed, which the borrowers must pay in addition to the principal amount.
A house is more than simply a place to live; it’s also a place to create memories with your family. Owning a house is critical to your current and future well-being. It is also a significant decision in one’s life. The cost of purchasing, building, renovating, or repairing a residential dwelling is extremely high these days. This is when a home loan is required. One of the most common products given by banks and NBFCs to customers is the home loan or housing loan. Home loans are also the most popular banking product and the one that secures the lender’s longest banking connection.
Customers can also choose variety of home loan options to meet their needs. The following is a list of the several types of house loans that banks and NBFCs offer:
Aside from the interest rate levied on house loan products, there are a variety of fees and charges associated with housing finance offered by various institutions. The following are the numerous fees that banks charge:
The exact loan amount will be decided based on the applicant’s income and repayment capacity, age, assets and liabilities, and the cost of the planned house/flat, among other variables. You can increase your loan eligibility by mentioning the following items:
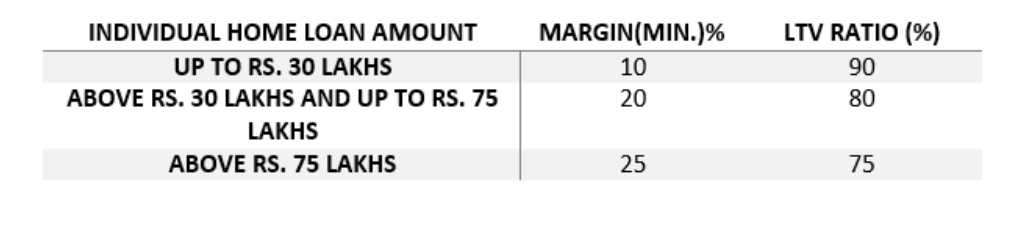
The majority of banks use this margin/loan-to-value ratio. The percentage of the property’s worth that will not be funded by the banks is referred to as the margin. The remainder will be given as a loan.
Share this Content
© 2021 All rights reserved
Ask Your Query